When Thr Light Touches Here We Can Drink Again
Why fainting happens, and how to nip it in the bud.
Faint, black out, swoon, laissez passer out. They're all names for the same thing — a temporary loss of consciousness followed by a fairly rapid and consummate recovery. It's frightening when information technology comes out of the blue, more than and then when it happens again and over again. The technical term, syncope (SIN-kuh-pee), comes from a Greek word that means to cut short or interrupt. What's beingness interrupted is claret catamenia to the brain.
Fundamental points
-
Fainting occurs when something interrupts claret flow to the encephalon. Although usually harmless, fainting tin cause injuries and sometimes signals a trouble with the heart or circulatory organization.
-
If you faint, it'due south worth talking with your dr., specially if there doesn't seem to be an explanation for the faint.
-
Tensing muscles in the legs and arms can sometimes stave off a faint; continuing or tilt grooming can assist some people get less susceptible to the crossed signals that crusade fainting.
Going, going, gone
Information technology is harder for the centre to pump blood up to the brain than down to the toes. Blood force per unit area helps overcome the down tug of gravity and button claret to the head.
We tend to recall of claret pressure level as a relatively stable entity. It isn't. It changes every fourth dimension you lot stand up, sit downwards, bend over, eat, sneeze, go to the bathroom, get stressed, relax, or heft a pocketbook of groceries. The man body is designed to counter these shifts and chop-chop bring blood pressure back to its usual betoken. This requires an intricate feedback organisation that involves sensors in the aorta and in the carotid arteries leading to the encephalon. These sensors stimulate a host of nerve and hormone signals that change how fast the heart beats, how much blood information technology pumps with each beat, and the wrinkle and relaxation of blood vessels. But some diseases, some drugs, and sometimes fifty-fifty aging interfere with these near-instantaneous corrections, causing temporary drops in blood flow to the brain.
Unlike most tissues, the brain doesn't store energy. Instead, it requires a abiding supply of sugar and oxygen. Halting blood menstruum for just iii to five seconds is enough to put the brain into an energy-conserving shutdown. The brain's signals to fretfulness and muscles stop, and the person slumps to the footing. Once the torso is horizontal, it's easier for the eye to pump claret to the head, and the brain "wakes up" again.
Many things can cause sudden depression catamenia to the encephalon that leads to fainting. The causes can exist grouped loosely into two camps: problems outside the centre (noncardiac syncope), which account for the majority of faints, and issues in the eye (cardiac syncope).
Getting to the heart of a faint
Figuring out what caused a fainting spell is the best way to prevent information technology from happening in the hereafter.
The nearly important piece of evidence is your story of what happened, especially if it can be corroborated by an eyewitness or two. Your description can suggest a vasovagal reaction (fainting due to standing too long in the heat, getting a shot, etc.), orthostatic hypotension (fainting when y'all stand up), or something more serious. A physical exam is in order no matter how straightforward the story.
An electrocardiogram (ECG) and echocardiogram are essential tests for evaluating anyone who has fainted. The echocardiogram can spot hidden problems in the left ventricle or other forms of structural middle disease that tin can cause fainting. The ECG tin notice irregularities in the heart's rhythm that could be the culprit. Unfortunately, capturing erratic heartbeats in the human activity is like finding the proverbial needle in a haystack. If you have fainted a few times for no apparent reason, and the ECG was "fine," your doctor might ask you to wear a device called a Holter monitor that continuously records the eye's electrical patterns for a 24-hour period. Longer-term monitoring can exist done with a wearable loop recorder or an implanted recorder. These devices constantly monitor the heartbeat just shop only the last several minutes. When a fainting spell hits, y'all printing a button to freeze the data in the recorder.
Another diagnostic test is the tilt exam, in which your blood pressure and heart rate are measured while lying flat on a moveable table, and then once again when the table is tilted and so you lot are almost, just not quite, standing upright.
Noncardiac causes
The virtually common reason for fainting arises from crossed wires between the brain and the part of the nervous arrangement (the vagus nerve) that regulates claret pressure and heart charge per unit. In response to some trigger, the claret vessels in your legs relax, making it difficult for blood to render to the heart. Blood begins pooling in the legs. To make matters worse, the heart slows downward just when it ought to exist speeding up. Blood force per unit area drops, and so do y'all. Triggers tin can range from fear, hurting, or intense emotional stress to having claret fatigued or standing for too long. Less mutual triggers include sneezing, going to the bathroom, lifting weights, a shirt collar rubbing against the side of the neck, and even playing a brass instrument.
Some people have faint-inducing drops in blood pressure when they get out of bed or stand up upward from a chair (called postural or orthostatic hypotension) or after eating (called postprandial hypotension). To understand postural hypotension, imagine your body as a tube of fluid. When you lie down, the fluid distributes itself fairly evenly from head to toe. When you stand up up, gravity pulls blood downwardly. Up to a quart of blood pools in the legs (that's well-nigh one-5th the total in the boilerplate developed), reducing the amount that is returned to the heart. The adjacent few heartbeats deliver less blood than usual, so blood pressure plummets. Standing later on sitting has much the same upshot. Dehydration can contribute to orthostatic hypotension, or sometimes even crusade it. A similar thing happens after eating. Every bit the body directs actress blood toward the stomach and intestines to help digestion, less is available to the middle, causing blood pressure level to fall.
Cardiac syncope
Fainting caused by trouble in the eye is more worrisome than noncardiac syncope. Rhythm problems are the near common culprit hither. The heart may beat too slowly (bradycardia) because of a defect in its electrical system or the influence of medications. It can also crush besides fast (tachycardia) considering of a rhythm disorder such as atrial fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia. The latter is especially dangerous, since it tin can turn into ventricular fibrillation, the most common cause of sudden cardiac abort.
Anything that obstructs blood menstruation through the heart can also lead to fainting. It could be a blocked or severely narrowed heart valve, a big blood clot, or even a tumor in the heart. Other cardiac causes of fainting include a severely enlarged heart (hypertrophic cardiomyopathy), a tear in the aorta, centre assault, or damage to the centre musculus.
Squeezing abroad a faint
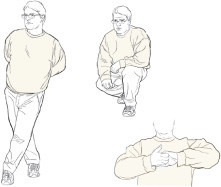
If you feel lightheaded or feel similar you lot might faint, try crossing your legs and tensing the muscles in the lower torso, squatting and tensing, or contracting the muscles in your artillery by clasping your hands and pulling. Each of these maneuvers can heave blood pressure. It might exist plenty to terminate the faint in its tracks, or information technology might but give you time to lie downwards or move to a prophylactic place.
Illustrations by Rob Flewell, with permission from the Periodical of the American College of Cardiology.
Fighting a faint
Most people get a few seconds of alert that a vasovagal faint is on its mode. They plough pale, go dizzy or giddy, and may experience nauseous or break out in a cold, clammy sweat. This early warning is sometimes enough time to nip a faint in the bud. Sitting or lying down often works, as does the proverbial "sit down and put your head betwixt your knees." Tensing the muscles in your hands, arms, and legs (encounter "Squeezing away a faint") can also help those who are composed enough to remember these maneuvers.
It may also exist possible to train your torso to fight faints. Writing in the May 12, 2009, Journal of the American College of Cardiology, Drs. David Yard. Benditt and John T. Nguyen of the University of Minnesota Medical Schoolhouse depict an exercise chosen tilt grooming. It involves standing with your back confronting a wall while your heels are virtually half-dozen inches from the wall (see "Tilt grooming").
If you know you will be in a situation in which you might faint — say you tend to pass out at the sight of blood but your girl wants y'all to exist with her when she gives birth to your offset grandchild — hither are a few things to do beforehand:
-
Drink a quart of juice and consume a pocketbook of potato fries. The thought is to load upwardly with fluid, so at that place is no take chances of dehydration.
-
Get some special stockings that put pressure on the calf and thigh muscles. This will help to prevent pooling of blood in the legs.
-
Have a reclining chair in the room, preferably one in which the legs tin exist raised to the level of the center if light-headedness occurs.
Tilt grooming
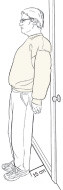
Some people can teach their bodies to overcome neurally mediated syncope, caused by crossed signals between the brain and the nervous arrangement. Stand with your back lightly against a wall while your heels are about six inches (xv centimeters) from the base of the wall. Do this for iii to five minutes without moving, twice a day. Every few days, add a minute or and then to the standing time until you tin can do 20- to 30-minute sessions without feeling faint. After that, endeavor to do 20 minutes of wall standing 3 to four times a week. Information technology's best to do this in a carpeted room, and to accept someone with you in case you faint.
Don't have it lying downwards
Most of the time, fainting is a harmless — though disconcerting — event. Sometimes, though, especially in older people, it can exist a warning sign of a potentially dangerous heart problem. For that reason, always let your doctor know if you lot've fainted, fifty-fifty if you think it was zilch to worry nearly. It's meliorate to be reassured it was "but a vasovagal spell" than to overlook something that could crusade a more serious problem downwardly the road.
As a service to our readers, Harvard Health Publishing provides access to our library of archived content. Please notation the date of last review or update on all manufactures. No content on this site, regardless of engagement, should always be used equally a substitute for direct medical communication from your doctor or other qualified clinician.
Source: https://www.health.harvard.edu/heart-health/When-the-lights-suddenly-go-out
0 Response to "When Thr Light Touches Here We Can Drink Again"
Post a Comment